Langflow Integration
Overview
Langflow is an open-source UI for LangChain, providing a visual way to build complex AI workflows by connecting components in a node-based editor. It allows users to experiment with language models, document loaders, and agents without coding.
Key Features
- Visual Flow Editor: Drag-and-drop interface for building LangChain applications
- Component Library: Extensive collection of pre-built nodes
- Real-time Testing: Test your flows as you build them
- Export Options: Export flows as Python code or JSON
- Custom Components: Add your own components to extend functionality
Use Cases
- Building RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems
- Creating autonomous AI agents with tool access
- Developing question-answering systems over custom data
- Prototyping complex LLM workflows before coding
- Teaching LangChain concepts visually
Setup Instructions
1. Install Langflow:
-
Option 1: Using pip
Terminal window pip install langflowlangflow run -
Option 2: Using Docker
Terminal window docker pull langflow/langflowdocker run -p 3000:3000 langflow/langflow -
Option 3: Using uv
Terminal window uv pip install langflowuv run langflow run
For details on the installation options, check the Langflow Getting Started Guide.
2. Access the Langflow UI:
- Open your browser and navigate to
http://localhost:3000or any other port you assigned.
- You should see the Langflow interface with a blank canvas and component library on the left side.
3. Create a New Flow:
- Click on “New Flow” to create a blank canvas
- Name your flow (e.g., “Custom LLM Integration”)
4. Create Custom Component:
- In the components panel on the left, select
+ New Custom Component - Edit the code for the custom component, replace it with below code to setup a BaseLLM for relaxAI endpoint.
from langchain.llms import OpenAIfrom langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAIfrom pydantic.v1 import SecretStr
from langflow.base.models.model import LCModelComponentfrom langflow.field_typing import LanguageModelfrom langflow.field_typing.range_spec import RangeSpecfrom langflow.inputs import BoolInput, DictInput, DropdownInput, IntInput, SecretStrInput, SliderInput, StrInputfrom typing import Dict, Any, Optional, List
class CustomRemoteLLMComponent(LCModelComponent): display_name = "Custom Remote LLM" description = "Connect to a custom remote OpenAI-compatible LLM API" icon = "Robot" name = "CustomRemoteLLM"
# Define available models for your custom API CUSTOM_MODEL_NAMES = [ "Llama-4-Maverick-17B-128E", "DeepSeek-R1-0528" # Add more models as needed ]
inputs = [ *LCModelComponent._base_inputs, IntInput( name="max_tokens", display_name="Max Tokens", advanced=True, info="The maximum number of tokens to generate. Set to 0 for unlimited tokens.", range_spec=RangeSpec(min=0, max=32000), value=1024, ), DictInput( name="model_kwargs", display_name="Model Kwargs", advanced=True, info="Additional keyword arguments to pass to the model.", ), BoolInput( name="json_mode", display_name="JSON Mode", advanced=True, info="If True, it will output JSON regardless of passing a schema.", ), DropdownInput( name="model_name", display_name="Model Name", advanced=False, options=CUSTOM_MODEL_NAMES, value=CUSTOM_MODEL_NAMES[0], ), StrInput( name="base_url", display_name="API Base URL", advanced=False, info="The base URL for your custom OpenAI-compatible API", value="http://api.relax.ai/v1", required=True, ), SecretStrInput( name="api_key", display_name="API Key", info="The API Key to use for authentication", advanced=False, required=True, ), SliderInput( name="temperature", display_name="Temperature", value=0.7, range_spec=RangeSpec(min=0, max=1, step=0.01) ), SliderInput( name="top_p", display_name="Top P", value=1.0, range_spec=RangeSpec(min=0, max=1, step=0.01), advanced=True, ), SliderInput( name="frequency_penalty", display_name="Frequency Penalty", value=0.0, range_spec=RangeSpec(min=-2.0, max=2.0, step=0.01), advanced=True, ), SliderInput( name="presence_penalty", display_name="Presence Penalty", value=0.0, range_spec=RangeSpec(min=-2.0, max=2.0, step=0.01), advanced=True, ), IntInput( name="seed", display_name="Seed", info="The seed controls the reproducibility of the job.", advanced=True, value=1, ), IntInput( name="max_retries", display_name="Max Retries", info="The maximum number of retries to make when generating.", advanced=True, value=5, ), IntInput( name="timeout", display_name="Timeout", info="The timeout for requests to the API in seconds.", advanced=True, value=60, ), BoolInput( name="streaming", display_name="Streaming", info="Whether to stream the response.", advanced=True, value=False, ), ]
def build_model(self) -> LanguageModel: # type: ignore[type-var] api_key = SecretStr(self.api_key).get_secret_value() if self.api_key else None base_url = self.base_url model_name = self.model_name temperature = self.temperature if self.temperature is not None else 0.7 max_tokens = self.max_tokens or 1024 model_kwargs = self.model_kwargs or {} json_mode = self.json_mode top_p = self.top_p frequency_penalty = self.frequency_penalty presence_penalty = self.presence_penalty seed = self.seed max_retries = self.max_retries timeout = self.timeout streaming = self.streaming
# Create a dict of kwargs to pass to the model model_params = { "model": model_name, "base_url": base_url, "api_key": api_key, "temperature": temperature, "max_tokens": max_tokens if max_tokens > 0 else None, "top_p": top_p, "frequency_penalty": frequency_penalty, "presence_penalty": presence_penalty, "seed": seed, "max_retries": max_retries, "request_timeout": timeout, "streaming": streaming, **model_kwargs, }
# Check if we're using a chat model (based on model name or other criteria) if any(chat_model in model_name.lower() for chat_model in ["chat", "gpt", "claude"]): # Initialize a ChatOpenAI for chat models output = ChatOpenAI(**model_params) # If JSON mode is enabled, bind the response format if json_mode: output = output.bind(response_format={"type": "json_object"}) else: # Initialize an OpenAI for completion models output = OpenAI(**model_params)
return output
def _get_exception_message(self, e: Exception): """Get a message from an OpenAI exception.
Args: e (Exception): The exception to get the message from.
Returns: str: The message from the exception. """ try: from openai import BadRequestError except ImportError: return None if isinstance(e, BadRequestError): message = e.body.get("message") if message: return message return None-
Click “Save” to create the custom component and run it to test the connection with the correct input of
RELAX_API_KEY. -
Save the relaxAI Custom component to use in your build flows.
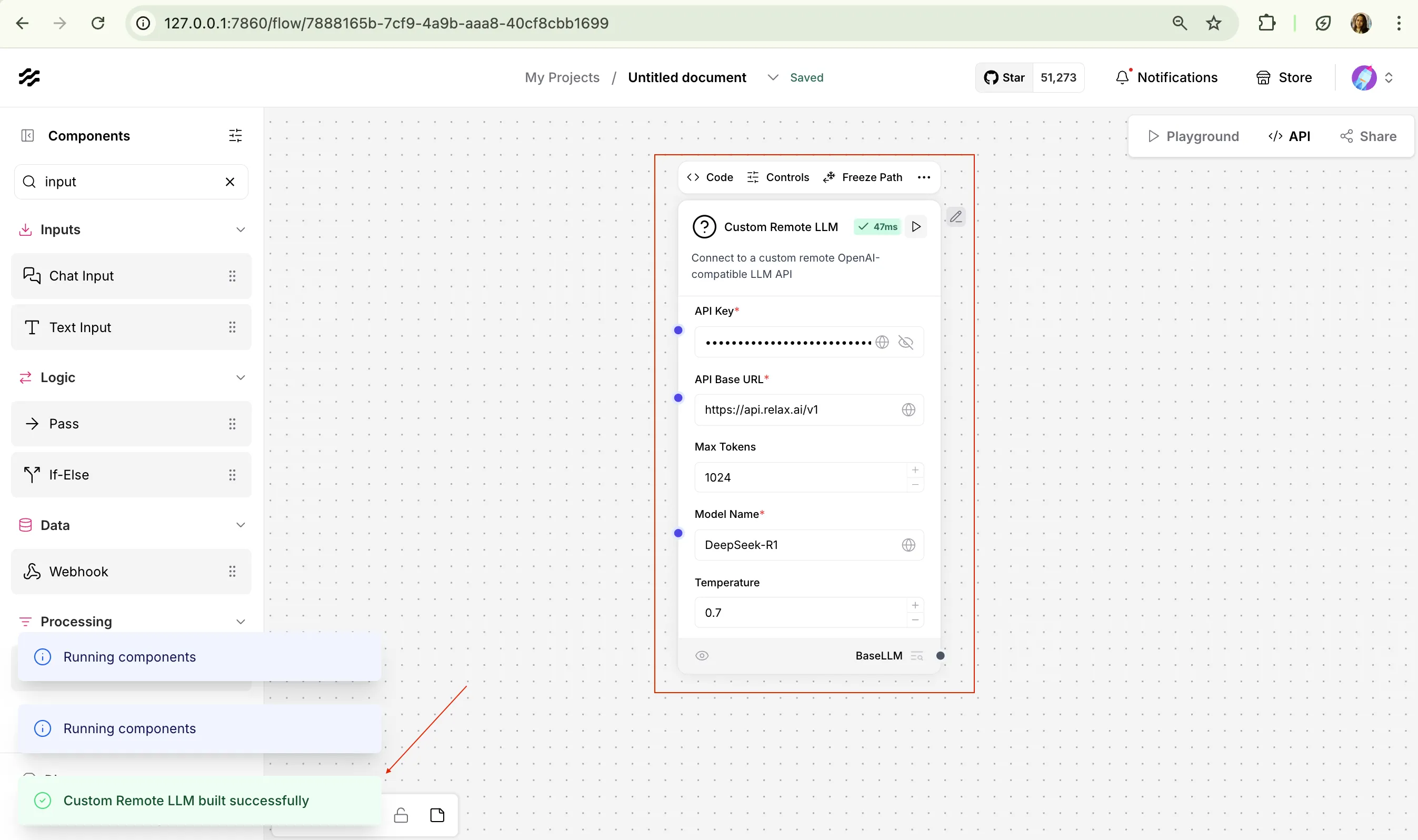
5. Set Up your sample flow:
- Select a agent/tool template and use that or create a custom flow.
- Drag the custom component you created onto the canvas
- Make sure to replace the llm with the custom component you created above.
Below is a sample blog writer agent flow that uses the custom component.

6. Set Up Prompt Template:
-
Configure the PromptTemplate with your desired prompt
-
Connect the PromptTemplate to your chat node
-
Configure the other necessary components as per the requirement of your agent/application.
7. Test Your Flow:
- Click the “Build” button to compile your flow
- Navigate to the “Playground” panel on the right
- Enter a test message and click send
- Verify that your custom LLM is responding correctly
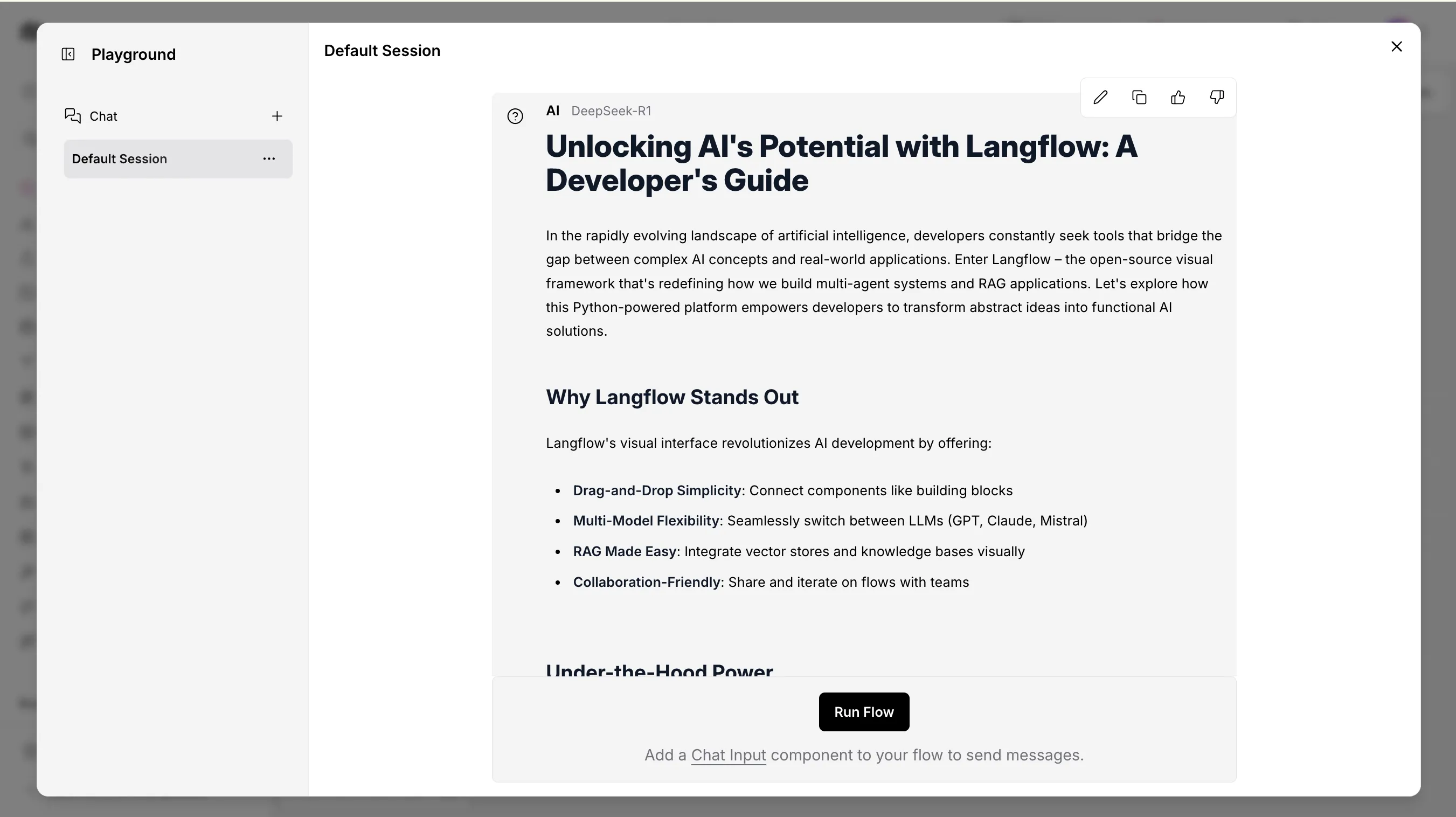
8. Save and Export:
- Click the “Save” button to save your flow
- Optionally, use “Export” to download the flow as Python code or JSON
Advanced Configurations
-
Creating Complex Flows:
- Add document loaders to incorporate external data
- Implement memory components for persistent conversations
- Use vector stores for RAG implementations
-
Custom Components:
- Create custom components with the Component Builder
- Import external Python packages for specialized functionality
-
Agents Setup:
- Combine LLM, Tools, and Agent components
- Configure tool access and reasoning capabilities
- Create autonomous systems that can perform tasks
Code Example
You can use your custom agent/tool as an API, below is an example of using out blog writer flow via curl.
curl -X POST \ "http://127.0.0.1:7860/api/v1/run/11de87e7-8a38-4d69-ab74-debcd6566336?stream=false" \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json'\ -d '{"input_value": "message", "output_type": "chat", "input_type": "text", "tweaks": { "ParseData-a2ZR0": {}, "Prompt-tjZKS": {}, "TextInput-XCQZW": {}, "ChatOutput-DhGYs": {}, "URL-jYZhf": {}, "CustomRemoteLLM (IAY4J)-aboXL": {}}}'Troubleshooting Tips
- If components aren’t connecting properly, check that output and input types match
- For API connection issues, verify your API key and endpoint URL
- Use the built-in debugging tools to see the data flow at each step
- If your flow becomes complex, consider breaking it into multiple smaller flows